Essential Maintenance Metrics Every Planner Needs to Know
Get Free Guide
Downtime Reports May Hide Problem Equipment

Are you doing regular machine downtime tracking? Having a lot of equipment downtime? Or is everything under control and there are hardly any maintenance emergencies?
Whatever the situation, operations managers and maintenance managers need to regularly identify problem equipment. These bad boys are the ones that cause frequent shutdowns or incur big maintenance costs.
When you many equipment it can be hard to do! This is where the equipment downtime reports or similar asset maintenance reports from your maintenance management software come in handy.
First – Identify Problem Equipment
1. Maintenance costs by equipment
Use reports from your CMMS program to get an idea of the total maintenance costs. Look at unplanned as well as planned maintenance costs over the last twelve months. Avoid looking at too short a period. Otherwise costs will be skewed if some equipment needs heavy maintenance only during certain times of the year. Find the most expensive machinery to maintain. Review the costs to see if anything seems out of line. Consider manufacturers cost estimates and prior years data to see if costs seem unusual.
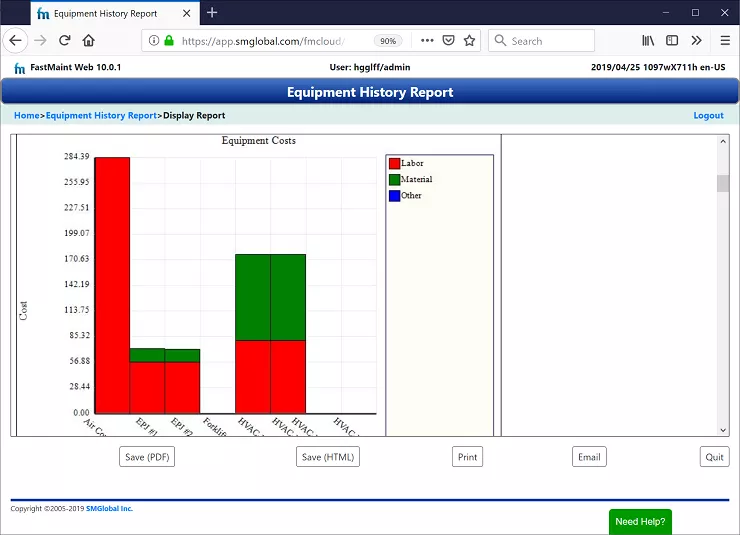
For instance, in FastMaint CMMS you can use the Equipment History report to get total maintenance costs (labor + material + other) of each equipment in a specified period (last month, last quarter and so on). This makes it easier to locate expensive equipment and find unusual variations in costs. For example, two similar equipment have widely varying maintenance costs.
Fig 1. Equipment history report from FastMaint CMMS showing total maintenance costs & duration
2. Equipment downtime duration
Look at equipment downtime reports for the past twelve months. If parts were not available or maintenance personnel were shifted to higher priority jobs, downtime can seem high for some equipment because it took a long time to fix. Filter out such equipment from your list.
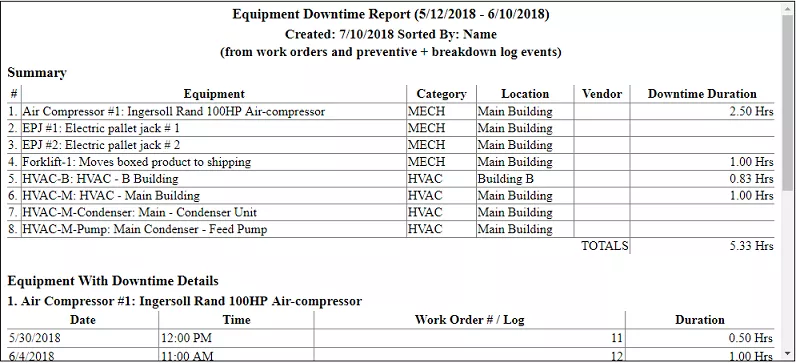
Below we have an Equipment Downtime report from FastMaint CMMS. In addition to the equipment downtime summary, it also contains work order and log details for each machine/ equipment. This single report thus allows you to locate problem equipment and drill in deeper by individual work orders and equipment log events to see the causes of high downtime.
Fig 2. Equipment downtime report from FastMaint CMMS showing downtime by equipment
3. Complaints history and maintenance work requests
Look at reported complaints and work requests over the past twelve months. Look for assets that have many complaints or many requests for maintenance work. Also review problem work orders. Sometimes replacement parts are not available or there are other delays with maintenance. This may result in many complaints or duplicated work requests since there is a delay in fixing the equipment.
For instance in FastMaint CMMS you can generate Work Order History reports and specify that you want to see only problem work orders. This allows you to quickly locate and filter out instances where there were problems due to other reasons.
4. Equipment statistics (e.g. MTBF, MTTF)
Statistics on equipment can be useful in many cases. They will not be so useful when you have many types of equipment. You will not be able to compare statistics easily. With similar equipment used in similar ways you can compare statistics. Investigate equipment that has statistics way out of line.
Using the Equipment History report or the Equipment Downtime report in FastMaint CMMS can be helpful to compare costs & downtime of similar assets and see why any are out of line.
Next – Find Breakdown Reasons
Once you have a list of problem equipment you should check further. Find the underlying causes. Equipment or machines that break down frequently could be failing for reasons such as:
1. Close to end of life
While it may be theoretically possible to keep on using equipment assets with a lot of ongoing maintenance, at some point it becomes too expensive to continue doing so. Internal metal fatigue, non availability of spare parts, lack of maintenance skills or newer equipment with better productivity and efficiency are reasons to consider replacing old machines. Replace any asset in your list that falls into this category.
2. Poor maintenance practices
This covers things like skipping preventive maintenance, using poor quality spares & supplies or maintenance technicians not knowing how to do the job correctly. Check if maintenance personnel keep replacing the same parts or frequently report issues during maintenance using some parts. Look for skipped preventive maintenance. Check work orders to make sure that maintenance procedures are being properly followed. Any equipment in your list that falls into this category needs a better preventive maintenance plan (7 Tips To Plan Equipment Preventive Maintenance). Maintenance personnel may need better training. If poor quality spare parts are causing problems it is time to look for vendors offering better quality.
3. Poor operational practices
This means that equipment operators are not using the equipment properly. Or the equipment is not designed for the loads being put on it. Feedback from maintenance technicians may mention operator errors. Improved operator training can help here. Equipment that is considered critical and fails frequently even if maintenance was properly done could be a sign of over loading of equipment. You may need to buy additional machines or look at making changes in operational flow to reduce peak loads.
4. Poorly designed or built
This means that the equipment has internal flaws that cause it to fail frequently. For example over heating because of inadequate cooling. If you have many similar equipment and they all seem to have frequent failures due to the same problem it could be sign of design or build issues. Do some research to find if other organizations using this equipment are also reporting similar problems. You may be able to get the manufacturer to fix these issues. Or consider buying better equipment from another vendor.
5. Incorrectly installed or setup
The equipment was not installed correctly. Or it was damaged during installation or initial startup. This may look similar to equipment with poor design or build. However, it will usually be isolated to only a few equipment out of many similar ones. Any research you do on other organizations reporting similar problems may not result in many similar complaints about the equipment. Comparing equipment statistics to manufacturers recommendations can also provide clues. You will need to check such equipment and do a complete re-install if necessary.
No CMMS? Cannot Get Downtime Tracking Reports?
You need to collect a lot of data from different reports from your maintenance management software. Do not have CMMS software or find the reports provided by your existing program hard to use? Get a web trial of FastMaint CMMS software in your web browser (or download a 30-day trial instead). Use the import feature to import much of your equipment from comma delimited files. Try out the different reports to see how to analyze equipment breakdown data. You cannot be successful without the right tools!
Free FastMaint CMMS TrialUseful Resources
- “Repair or replace? Best Strategies to Reduce Maintenance Costs” from the Management Insight section in FaciltiesNet.
- “Lean Thinking and Methods” from the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) which has tips on reducing & managing breakdowns using lean manufacturing methods.
Essential Maintenance Metrics Every Planner Needs to Know
Get Free Guide
