Want useful metrics for your maintenance program?
Get Key Maintenance Metrics

CMMS Software aka maintenance management software helps organizations manage maintenance of their equipment, facilities and other enterprise assets.
But that’s just part of the story…
Companies that use a maintenance program can see a significant reduction in the maintenance costs. In addition they can save costs due to fewer equipment breakdowns. They also see improved equipment and facility performance that results in better quality and higher customer satisfaction.
A CMMS program is not just useful to manage breakdown or corrective maintenance. It can also help us schedule & track preventative maintenance. What are the preventive maintenance scheduling options that we can use to do needed maintenance on equipment & other assets?
Common Ways To Schedule Preventive Maintenance
1. Schedule by dates
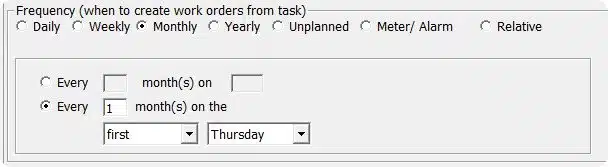
This is the most frequent way of scheduling preventive maintenance. We can specify a work order frequency e.g. every Wednesday, every 45 days, every 6 months and so on. While fairly easy to setup, the downside is that we may schedule maintenance less optimally than required.
What could this mean?
Say there is a plant shutdown. The equipment does not run. We end up scheduling maintenance too early. Or there is a production deadline. The machine runs for longer hours than normal. We will schedule maintenance too late. Preventive maintenance done too late runs the risk of an equipment breakdown. This is a big risk especially when we have a production deadline!
2. Schedule by meter readings or equipment usage
We schedule preventative maintenance based on the machine usage. For example on a vehicle we schedule an oil change after every 3000 miles, on a machine making widgets it could be after every thousand widgets produced and so on. This can produce a more optimal maintenance schedule. However, it can involve more work because we need to enter meter readings manually or by importing them.
Another option is to use something called “estimated meter use” which is available in FastMaint CMMS software. Here the system estimates equipment usage and schedules maintenance based on a work calendar. This allows us to enter working times, holidays and other shutdown times into the calendar. Then the maintenance program can estimate usage and schedule maintenance dates for different equipment that use this calendar.
3. Schedule relative to another work order or task
This means that a maintenance task is scheduled some number of days after another maintenance task work order is completed. This is useful if we need to chain work orders together. For instance when a maintenance job consists of two different tasks done by two different sub-contractors.
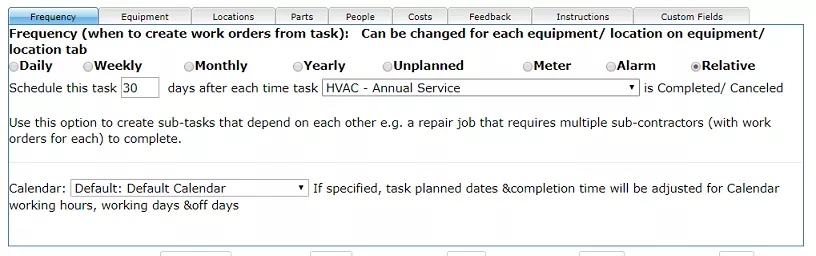
We can also schedule a task based on its prior completion. For example, we can schedule a preventive maintenance task 30 days after the previous time it is completed.
4. Schedule based on an alarm condition
This allows us to define some external condition, say an alarm. When an alarm occurs it means that we have to do some preventive maintenance. For instance an overheat condition on a machine means that we have to lubricate all bearings.
This could also mean alarms or maintenance requests scheduled using a condition monitoring or predictive maintenance system. These can be external specialized systems separate from the maintenance management software. They analyze equipment data to flag potential issues or predict that maintenance is due. Such systems can raise something similar to an alarm condition. This can be used by the CMMS software to schedule multiple maintenance tasks on different enterprise assets.
Reduce Maintenance Schedule Dependencies
We can see from above there are a gamut of ways to schedule and manage preventive maintenance on different assets. Of these “scheduling by dates“, “scheduling by estimated meter use” and “scheduling based on another work order” offers the easiest way to schedule maintenance. This avoids depending on external systems for input (meter readings, alarms, etc.).
Preventive maintenance scheduling can become an issue if external systems are unreliable. There could be similar problems if we use a manual process that involves a lot of effort to bring the information in.
Just think about it…
For example someone has to manually collect meter readings and input them in. This sounds like something we could forget to do especially when things are busy. What if we have an automatic input process? We could still lose some alerts or readings due to failures in the data import or collection. All this means that we will not schedule needed maintenance.
Don’t look at me like that!
This means we will need to make sure that any equipment or facilities that have such maintenance scheduled, will not suffer catastrophic failure if some preventive maintenance is missed because input from an external system was not provided in time. While it may be rare – it can happen!
CMMS Software Selection Tips
Are you looking for good maintenance scheduling software to help create a preventive maintenance schedule at your organization? You will find our free “CMMS Selection Guide” very helpful. It has a variety of tips and advice on selecting a good maintenance software program for your needs. This will make finding the right CMMS package faster and less confusing.
Free CMMS Software Selection GuideAdditional Reading
- 7 Breakdown Maintenance Planning Tips
- Preventive Maintenance Scheduling – When Is It Excessive?
- CMMS ROI Calculator: Calculate your CMMS cost savings
Want useful metrics for your maintenance program?
Get Key Maintenance Metrics
